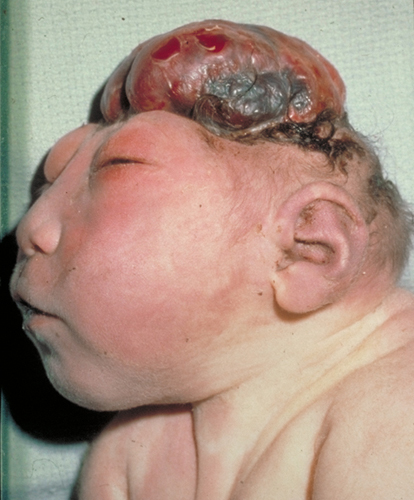
Definition:
Absence of the calvaria above the bony orbits. May be associated with absence of cerebral hemisphere.
Incidence:
1/1000 live births.
Pathogenesis:
Failure of closure of cephalad neural tube at 25 - 27 days post conception.
Risk of Recurrence:
2 - 4 % with 1 affected siblings. 10% with 2 affected siblings.
Diagnosis (Antenatal):
- Absent bony calvaria
- Orbits well visualized
- Absence of supratentorial brain
- Residual brain
- Associated polyhydromnios, due to decreased fetal swallowing
- Associated spina bifida
- Spina bifida
- Urinary tract anomalies
- Cleft lip / palate
- GIT anomalies (ie. omphalocoele, intestinal aganglionosis)
- Cardiac anomalies
Prognosis:
Incompatible with life. Some may live up to a week postnatally.
Prevention:
Folic acid supplements, recommended 4 mg per day a month preconception and 3 months after.
With-holding anticonvulsants (folic acid antagonist, ie. valproate, carbamezapine, phenytoin, trimetoprim)
References
1. Nyberg, David A., et al., Diagnostic Imaging of Fetal Anomalies, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2003.
2. Tomita T., et al., Anencephaly, UpToDate Article, 2012.
Future Topics:
- Folic acid in prevention of neural tube defects.
- Feasibility of organ donation of anencephalic babies
- Spina bifida and other neural tube defects.

No comments:
Post a Comment